python 读取带有struct的NASA数据
实现电池数据的提取以及对Struct结构的使用介绍
·
说明:
采用的数据集是NASA的B0005.mat 为了方便degub 因此只选择了前3个充放电周期进行代码测试,且对原始6个变量进行切片处理
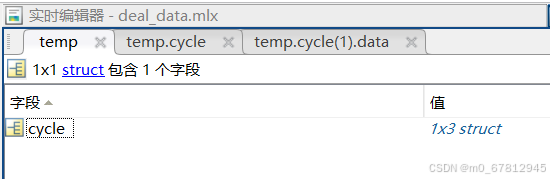
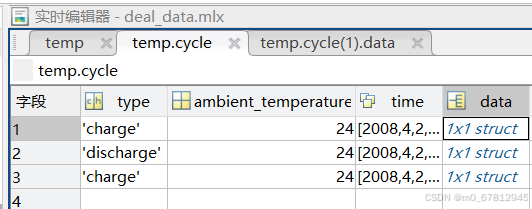
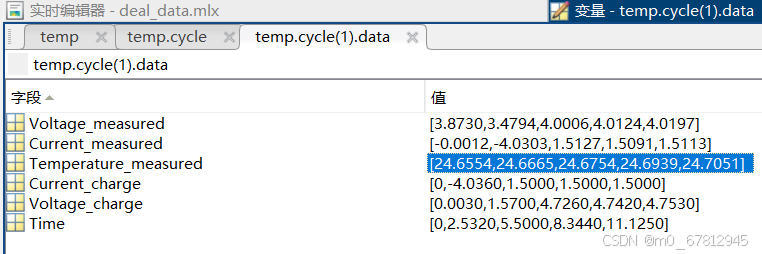
1.读取数据集代码:
data = scipy.io.loadmat(file)
filename = file.split(".")[0].split("/")[2] # B0005
# print(filename)
col = data[filename]
col = col[0][0][0][0]
size = col.shape[0]
data = []
for i in range(size):
k = list(col[i][3][0].dtype.fields.keys())
d1, d2 = {}, {}
if str(col[i][0][0]) != 'impedance':
for j in range(len(k)):
t = col[i][3][0][0][j][0]
l = [t[m] for m in range(len(t))]
d2[k[j]] = l
d1['type'], d1['temp'], d1['time'], d1['data'] = str(col[i][0][0]), int(col[i][1][0]), str(
convert_to_time(col[i][2][0])), d2
data.append(d1)
return data但是由于里面这么多结构 很多 [0] [0]啥的看不懂,因此对探索一下数据读进来是啥规律
data = scipy.io.loadmat(file)
filename = file.split(".")[0].split("/")[2] # B0005
'''
python中读取mat数据说明,总共可以分为三层结构,其中第一层为ndarray,第二层也为ndarray,第三层是数据层np.void 类似于dict,可以通过下标或者字段名来实现访问
然后使用下标访问的时候,获取的数据类型一般也是一个ndarray数组,因此想要获取里面的值可以通过下标的方式获取 这个时候一般就是下表为[0]实现获取,不行的话打印type看看用啥下标
a = data[filename]
print(f"01 a.shape:{a.shape}\na.type:{type(a)}\n")
01 a.shape:(1, 1)
a.type:<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
b = a[0]
print(f"02 b.shape:{b.shape}\nb.type:{type(b)}\n")
02 b.shape:(1,)
b.type:<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
c = a[0][0]
print(f"03 c.shape:{c.shape}\nc.type:{type(c)}\n")
03 c.shape:()
c.type:<class 'numpy.void'>
d = a[0][0][0]
print(f"04 d.shape:{d.shape}\nd.type:{type(d)}\n")
04 d.shape:(1, 3)
d.type:<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
e = a[0][0]['cycle']
print(f"05 e.shape:{e.shape}\ne.type:{type(e)}\n")
05 e.shape:(1, 3)
e.type:<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
上述几个操作证明了struct结构读取进来的时候为三层结构
'''
'''
下面证明访问void结构的时候 里面数据也为ndarray结构
'''
col = data[filename]
col = col[0][0][0][0]
size = col.shape[0]
tmp = data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]
is_print = True
if is_print:
print(f"size:{size}\ntmp.shape:{tmp.shape}tmp.len:{len(tmp)}") # size:3 tmp.shape:() tmp.len:4
# 检查两者是否相同
print(np.array_equal(col, tmp)) # False
print(type(col), type(tmp)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> <class 'numpy.void'>
print(col.shape, tmp.shape) # (3,) ()
print(col[0]['type'])
print(tmp[0])
data = []
for i in range(size):
k = list(col[i][3][0].dtype.fields.keys())
# ['Voltage_measured', 'Current_measured', 'Temperature_measured', 'Current_charge', 'Voltage_charge', 'Time']
d1, d2 = {}, {}
# temp = col[i] type <class 'numpy.void'>
# a = col[i][0] # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> #['charge']
# b = col[i][0][0] # <class 'numpy.str_'> # charge
# tmp = col[i]['type'][0] # charge
# 在这个地方a、b 的时候可以看到里层结构就是ndarray结构的
if str(col[i]['type'][0]) != 'impedance':
for j in range(len(k)):
# print(f"03 type:{type(col[i][3][0][0][j])}\nvalue:{col[i][3][0][0][j]}")
# <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[3.87301722 3.47939356 4.00058782 4.01239519 4.01970806]]
t = col[i][3][0][0][j][0]
# print(f"04 value:{t}\ntype:{type(t)}\n")
# [3.87301722 3.47939356 4.00058782 4.01239519 4.01970806] <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
d2[k[j]] = t.tolist()
d1['type'], d1['temp'], d1['time'], d1['data'] = str(col[i][0][0].item()), int(col[i][1][0].item()), str(
convert_to_time(col[i][2][0])), d2
data.append(d1)进一步验证猜想:
'''
first = data[filename]
a = data[filename][0][0]
b = data[filename][0][0]['cycle']
c = data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]
d = data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]['data']
e = data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]['data'][0][0]
f = data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]['data'][0][0][0]
f_tmp = data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]['data'][0][0]['Voltage_measured']
g = data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]['data'][0][0][1]
print(f"first:{type(first)}\n{first}") # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[(array([[ (array(['charge'], dtype='<U6')) ]]) )]]
print(f"a:{type(a)}\n{a}") # <class 'numpy.void'> (array([[ (array(['charge'], dtype='<U6')) ]]) )
print(f"b:{type(b)}\n{b}") # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[( (array(['charge'], dtype='<U6')) ]]
print(f"c:{type(c)}\n{c}") # c:<class 'numpy.void'> (array(['charge'], dtype='<U6')
print(f"d:{type(d)}\n{d}") # d:<class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[(array([[3.87301722, 3.47939356, 4.00058782, 4.01239519, 4.01970806]]) ]]
print(f"e:{type(e)}\n{e}") # e:<class 'numpy.void'> (array([[3.87301722, 3.47939356, 4.00058782, 4.01239519, 4.01970806]]) )
print(f"f:{type(f)}\n{f}") # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[3.87301722 3.47939356 4.00058782 4.01239519 4.01970806]]
print(f"f_tmp:{type(f_tmp)}\n{f_tmp}") # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[3.87301722 3.47939356 4.00058782 4.01239519 4.01970806]]
print(f"g:{type(g)}\n{g}") # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[-1.20066070e-03 -4.03026848e+00 1.51273065e+00 1.50906328e+00,1.51131819e+00]]
'''总结
使用scipy.io 读取mat文件的时候,使用 [0] [0] 可以实现读取到类似于dict结构的numpy.void结构。 使用完2层[0] [0] 之后就得到了对应的数据,此时可以通过下标[0]、[1] 或者字段名的方式获取数据 此时获得的数据集类型为ndarray结构,如果获取类型数据看看里面到底有多少层[[]] 在使用代码
例如使用 data[filename][0][0]['cycle'][0][0]['data'][0][0]
01.第一个组合得到cycle这一个大表格的数据,如果里面还有其他字段也可以直接使用下标或者字段名读取,例如data[filename][0][0]['cycle'] / data[filename][0][0][0] / data[filename][0][0]['XXX'] XXX 表示其他字段值
02.第二个[0][0] 实现读取第二个表格里面的数据大小
03.第三个[0][0] 实现读取第三张图里面的所有数据值更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容









所有评论(0)